HOG论文阅读
Histograms of Oriented Gradients for Human Detection
用于人类检测的定向梯度直方图
Abstract
我们在研究一个具有鲁棒性的视觉对象的特征,使用线性SVM检测人类作为测试。
HOG比其他边缘检测的特征好等等不啦不啦
研究了HOG计算的各个阶段,认为精细的梯度,较好的方向bin,(就那个方向分成nbins),相对粗略的空间合并以及overlapping descriptor blocks中的高质量局部对比度归一化对于取得良好的结果都很重要。
1 Introduction
为了检测各种情况下的人类,一个鲁棒性的特征是十分重要的。
HOG表现很好。
2 PreviousWork
Papageorgiou et describe a pedestrian detector based on a polynomial SVM using rectified Haar wavelets as input descriptors, with a parts (subwindow) based variant in [17].
Depoortere et give an optimized version of this [2]. Gavrila & Philomen[8] take a more direct approach, extracting edge images and matching them to a set of learned exemplars using chamfer distance. This has been used in a practical real-time pedestrian detection system [7].
Viola et al [22] build an efficient moving person detector, using AdaBoost to train a chain of progressively more complex region rejection rules based on Haar-like wavelets and space-time differences.
Ronfard et [19] build an articulated body detector by incorporating SVM based limb classifiers over 1st and 2nd order Gaussian filters in a dynamic programming framework similar to those of Felzenszwalb & Huttenlocher [3] and Ioffe & Forsyth
Mikolajczyk et al [16] use combinations of orientationposition histograms with binary-thresholded gradient magnitudes to build a parts based method containing detectors for faces, heads, and front and side profiles of upper and lower body parts.
3 Over view of the Method
这个方法是基于评估很好normalized的局部HOG特征的在一个密集格子区域的方法。
基本思想是,即使没有相应梯度或边缘位置的精确知识,通常也可以通过局部强度梯度或边缘方向的分布来很好地表征局部对象的外观和形状。
在实践中,这是通过将图像窗口划分为较小的空间区域(“单元”)来实现的,对于每个单元,在单元像素上累积梯度方向或边缘方向的局部一维直方图。
为了更好地保持照明,阴影等不变,在使用局部响应之前对它们进行对比度归一化也很有用。
这可以通过在较大的空间区域(“块”)上累积局部直方图“能量”的度量,然后使用结果对块中的所有单元进行归一化来完成。
我们将归一化描述符块称为定向梯度直方图(HOG)描述符。
用密集的(实际上,重叠的)HOG描述符网格平铺检测窗口,并在传统的基于SVM的窗口分类器中使用组合的特征向量,可以得出我们的人工检测链(见图1)。
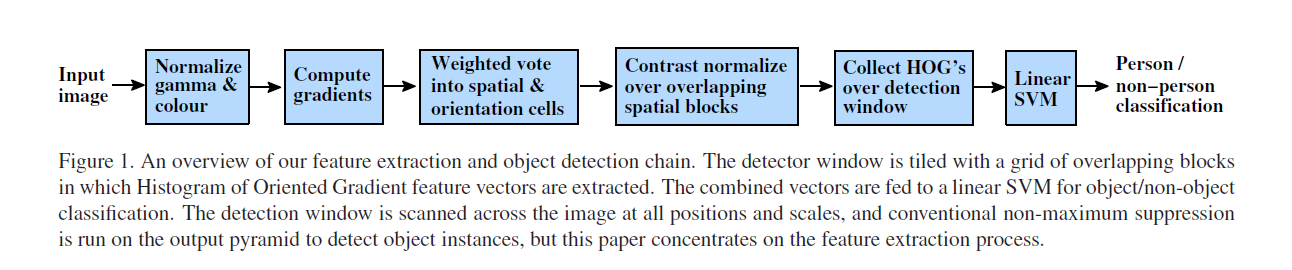
4 Data Sets and Methodology
Datasets.
使用的dataset是下面两个
MIT
INRIA
Methodology.
正负样本选取,评价指标制定
5 OverviewofResults
,,
6 Implementation and Performance Study
图片是RGB空间的没有gamma校正
使用[-1, 0, 1]的梯度滤波器没有smoothing。
线性的梯度投票到9哥方向bins中,0-180度
16 * 16的blocks包含4个8 * 8的cells
Gaussian spatial window with σ = 8pixel;
L2-Hys (Lowe-style clipped L2 norm) block normalization;
block spacing stride of 8 pixels (hence 4-fold coverage of each cell);
64×128 detection window;
linear SVM classifier.
实验结论:
为了更好的性能,应该使用更精细的导数,不使用平滑措施,更多的方向bins,和中等大小。很好的归一化后的重叠着的描述block。
6.1 Gamma/Colour Normalization
归一化带来的影响不大
6.2 Gradient Computation
检测器性能对计算梯度的方式很敏感,但是最简单的方案却是最好的方案。
Simple 1-D [−1, 0, 1] masks at σ=0 work best.
对于彩色图像,我们为每个颜色通道计算单独的渐变,然后将范数最大的渐变作为像素的渐变矢量。
6.3 Spatial / Orientation Binning
每个像素计算出的梯度方向,加权投票到对应的方向bins中。
cells可以是矩形或放射状(对数极性的扇区)。
在实践中,使用梯度大小本身可以提供最佳结果。取平方根会稍微降低性能,而使用二进制边缘状态投票会明显降低性能。
6.4 Normalization and Descriptor Blocks
由于光照和前景-背景对比度的局部差异,渐变强度会在很大范围内变化,因此有效的局部对比度归一化对于实现良好性能至关重要。
这似乎是多余的,但是良好的规范化至关重要,并且包括重叠部分可以显着提高性能。
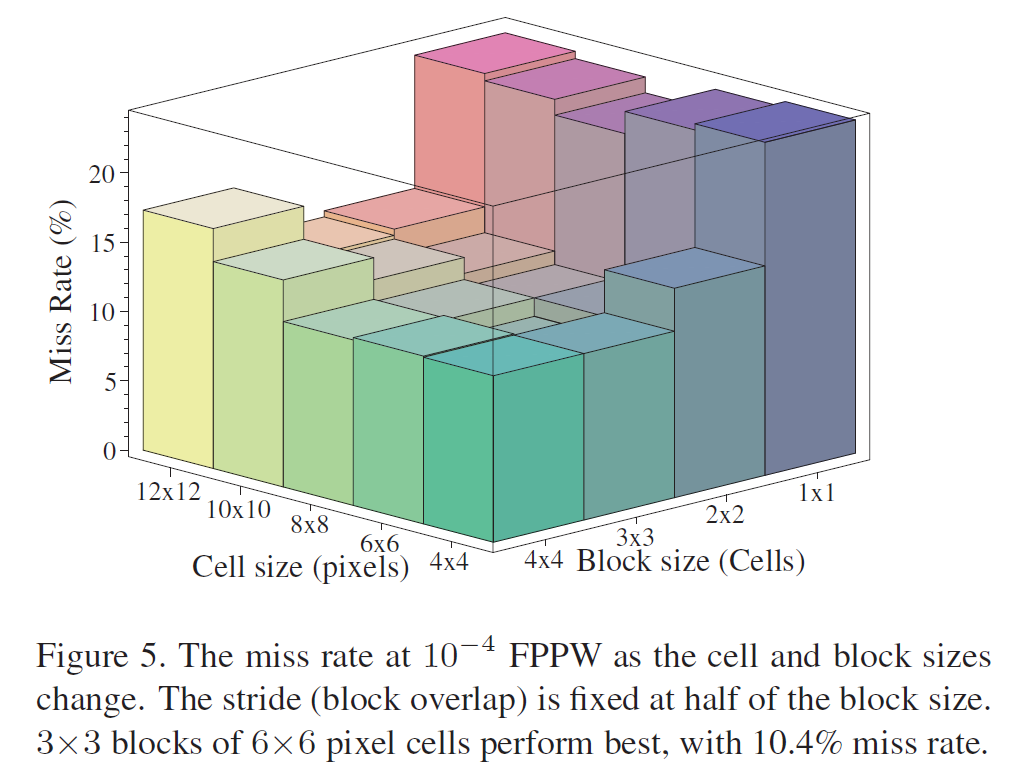
对于人体检测,6×6像素cell的3×3的cell block表现最佳。
Gaussian with σ = 0.5 ∗ block width.
R-HOG rectangle HOG
C-HOG circular HOG
Block Normalization schemes.
块归一化
Let v be the unnormalized descriptor vector
L2_norm
$$ v -> \frac{v}{\sqrt{||v||^2_2+\delta^2}} $$
L2_Hys
L2-Hys, L2-norm followed by clipping (limiting the maximum values of v to 0.2) and renormalizing
L1-norm
$$ v -> \frac{v}{||v1||_1+\delta} $$
L1-sqrt
$$ v -> \sqrt{\frac{v}{||v||_1+\delta}} $$
6.5 DetectorWindow and Context6.5 DetectorWindow and Context
Our 64×128 detection window includes about 16 pixels of margin around the person on all four sides.
this border provides a significant amount of context that helps detection
6.6 Classifier
By default we use a soft (C=0.01) linear SVM trained with SVMLight Using
a Gaussian kernel SVM increases performance by about 3% at 10−4 FPPW at the cost of a much higher run time.